Electronic Common Technical Document (eCTD) 4.0
What is eCTD 4.0?
The Electronic Common Technical Document (eCTD) 4.0 is the latest standard developed by the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) for submitting regulatory information electronically. It replaces eCTD version 3.2.2 with a more flexible, data-rich format that enables granular content updates, improved interoperability, and better lifecycle management across global regulatory agencies.
Unlike its predecessor, eCTD 4.0 adopts the HL7 Regulated Product Submission (RPS) message standard, making it possible to exchange structured content at the component level and link updates directly to impacted data without resubmitting entire dossiers.
Why it Matters in Pharma Today
- Granular content management — Agencies and sponsors can update individual sections or components rather than re-authoring complete submissions.
- Global regulatory alignment — Supported by ICH, FDA, EMA, PMDA, and other major agencies, ensuring a harmonised submission approach.
- Lifecycle efficiency — Improves tracking of submission history, variations, and regulatory queries over the product’s lifetime.
- Interoperability — Built on HL7 RPS, enabling tighter integration with internal authoring tools, regulatory databases, and agency systems.
- Future-proofing — Designed to support evolving regulatory requirements, structured data elements, and automation in submission assembly.
Global Landscape
| Region/Body | Governing Entity |
Adoption Status / Timeline |
| ICH | ICH M8 EWG | Maintains eCTD 4.0 specification and implementation guidance. |
| United States (FDA) | CDER & CBER | Draft guidance published; pilot submissions underway. Full adoption expected late 2020s. |
| European Union (EMA) | EMA | Implementation roadmap published; transition period from 3.2.2 in progress. |
| Japan (PMDA) | MHLW/PMDA | Planning phase for migration from 3.2.2; no official go-live date yet. |
| Canada (Health Canada) | Health Canada | Monitoring ICH timelines; adoption likely post-EMA/FDA rollout. |
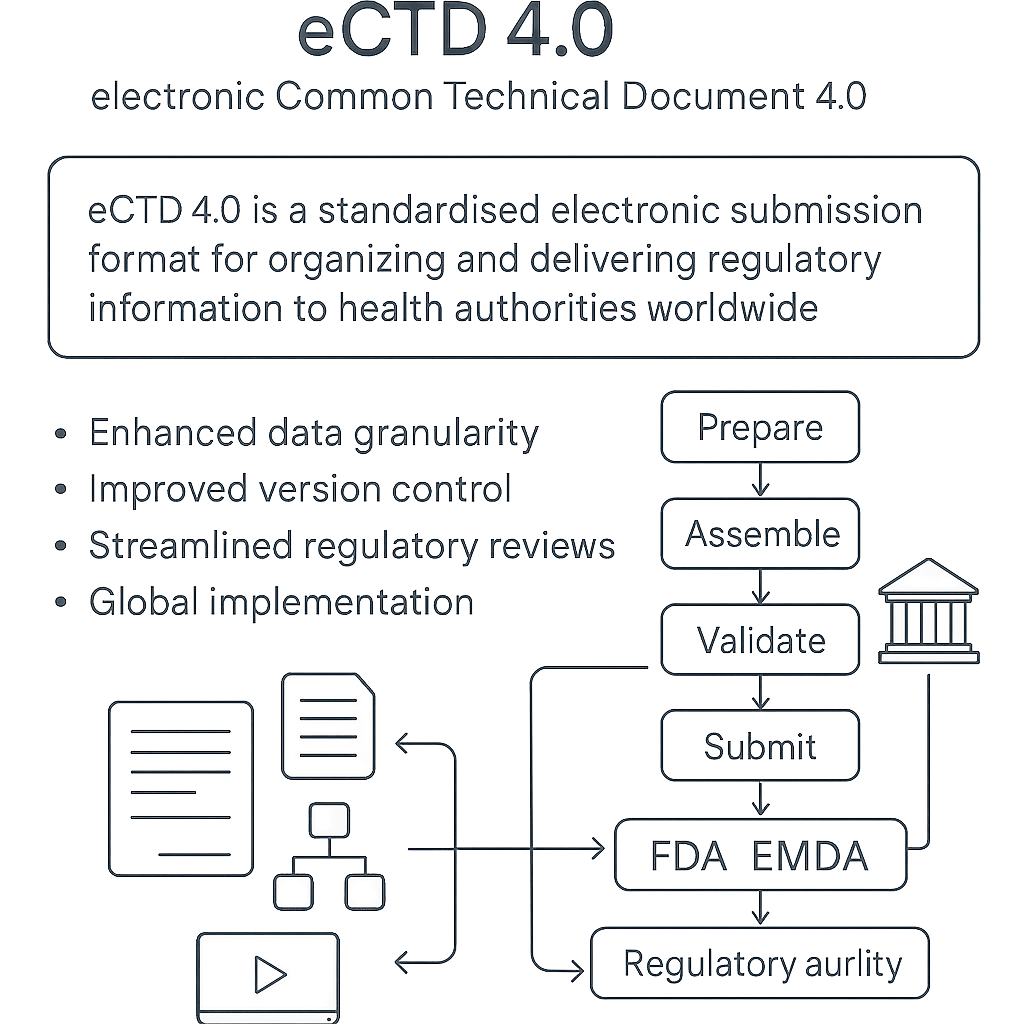
How eCTD 4.0 Works in a Component-Based Authoring Model
- Author — Create regulatory content as structured, metadata-rich components aligned to eCTD headings and subheadings.
- Assemble — Use metadata mapping to automatically place components into the correct eCTD sections.
- Validate — Apply agency-specific and ICH M8 validation rules to ensure completeness and compliance.
- Submit — Package and transmit via secure electronic gateways (e.g., FDA ESG, EMA Gateway).
- Track — Monitor agency receipt, acknowledgement, and processing status; link feedback to specific components.
- Update — Replace or amend only the affected component(s) without resubmitting the full dossier, enabling more efficient regulatory change management.
Typical Component Mapping in eCTD 4.0
- Module 1 (Regional Administrative Information) — MAH details, application forms, labeling.
- Module 2 (Summaries) — Quality Overall Summary (QOS), Nonclinical and Clinical Overviews.
- Module 3 (Quality) — CMC data, manufacturing sites, analytical procedures.
- Module 4 (Nonclinical Study Reports) — Pharmacology, toxicology.
- Module 5 (Clinical Study Reports) — Protocols, CSR, datasets.
Top eCTD 4.0 FAQs
The Electronic Common Technical Document (eCTD) 4.0 is the latest global standard for submitting regulatory information electronically. Developed by the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH), it replaces eCTD 3.2.2 with a data-driven, component-based format that improves lifecycle management, interoperability, and content traceability across regulatory authorities worldwide.
eCTD 4.0 introduces a more granular, automated, and harmonized submission process. It enables sponsors and agencies to update specific components instead of reauthoring full dossiers, improving speed, compliance, and transparency. This shift supports global digital transformation initiatives led by the FDA, EMA, PMDA, and Health Canada, and aligns with ICH’s push toward data-centric regulation.
The most significant change is the adoption of the HL7 Regulated Product Submission (RPS) message standard.
-
3.2.2: Document-level updates, limited metadata, manual re-submission.
-
4.0: Component-level updates, richer metadata, and traceable change control—allowing efficient lifecycle management and regulatory alignment.
Global rollout is staged:
-
ICH (M8 EWG): Maintains specifications and governance.
-
FDA (U.S.): Pilots in progress; full adoption expected late 2020s.
-
EMA (EU): Transition roadmap published; migration from 3.2.2 underway.
-
PMDA (Japan): In planning phase.
-
Health Canada: Expected to align post-EMA/FDA rollout.
Together, these initiatives drive global harmonization of electronic submissions.
Because eCTD 4.0 tracks and links updates at the component level, companies can modify only the affected content block—such as a manufacturing site or label—without resubmitting the full dossier. This significantly reduces review timelines and supports real-time regulatory collaboration and version traceability.
SCA enables content to be authored once, governed centrally, and reused everywhere. In an eCTD 4.0 environment, SCA allows modular, metadata-tagged content to flow directly into the correct submission sections. This integration ensures compliance by design, accelerates updates, and supports automation through HL7 RPS mapping.
Docuvera’s governance-first structured content platform is designed for the next generation of digital submissions. It:
-
Authors content as reusable, machine-readable components aligned to eCTD headings.
-
Embeds metadata, validation rules, and audit trails at creation.
-
Integrates with RIM, QMS, and submission gateways (FDA ESG, EMA Gateway).
This ensures eCTD 4.0-compliant content that is regulator-ready, interoperable, and traceable across global markets.